Throttle position sensor are critical components in modern automotive engines, providing critical information about throttle position to the Engine Control Unit (ECU). Throttle Position Sensors, Their Functions, Types, Principles of Operation, Applications and Challenges. TPS plays a vital role in maintaining engine performance, optimizing fuel efficiency and reducing emissions. As automotive technology continues to advance, TPS remains a key factor in the quest to improve automotive performance and environmental sustainability.
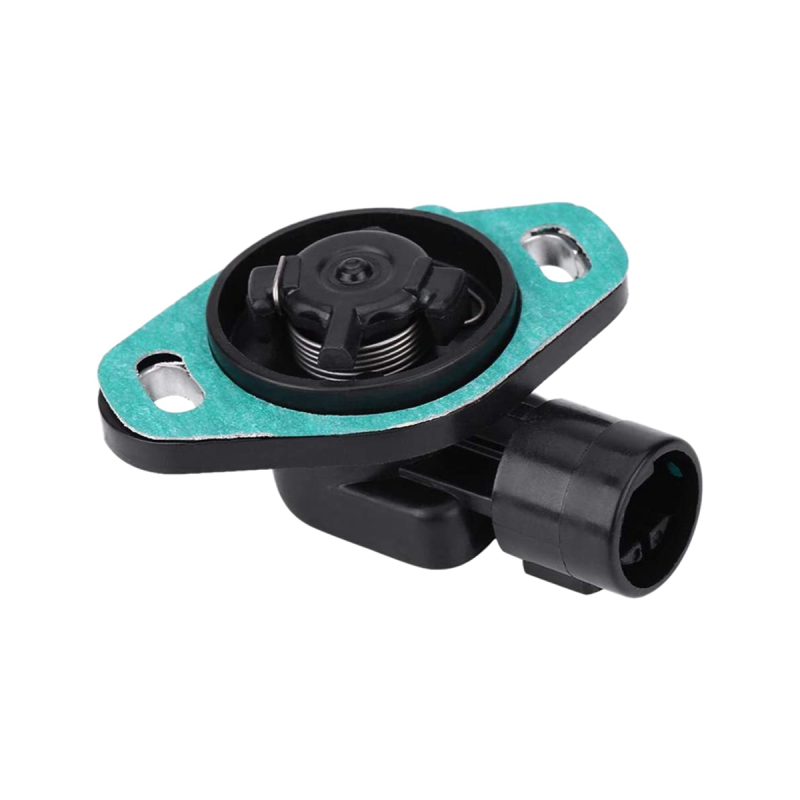
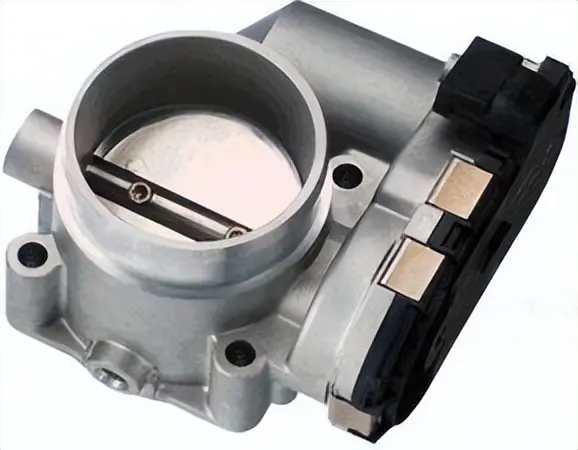
Throttle Position Sensors (TPS) are an essential part of electronic fuel injection systems used in most modern internal combustion engines. It monitors the position of the throttle plate and communicates this information to the Engine Control Unit (ECU). The ECU uses TPS data to calculate the proper air-fuel mixture, ignition timing and engine load, ensuring the best performance of the engine under various driving conditions. There are two main types of throttle position sensors: potentiometric and non-contact.
Potential TPS consists of a resistive element and a wiper arm connected to the throttle shaft, when the throttle plate is opened or closed, the wiper arm moves along the resistive element, changing the resistance and generating a proportional to the throttle position voltage signal. This analog voltage is then sent to the ECU for processing. Non-contact TPS, also known as Hall Effect TPS, uses the principle of Hall Effect to measure the throttle position. It consists of a magnet attached to the throttle shaft and a Hall effect sensor.
As the magnet rotates with the throttle shaft, it generates a magnetic field, which is detected by the Hall effect sensor, producing an output voltage signal. Compared to potentiometric TPS, non-contact TPS offers higher reliability and durability because there are no mechanical parts in direct contact with the throttle shaft. The working principle of TPS is to convert the mechanical movement of the throttle valve into an electrical signal that the electronic control unit can recognize.
As the throttle plate rotates, the wiper arm on the potentiometer TPS moves along the resistance trace, changing the voltage output, and when the throttle is closed, the resistance is at its maximum, resulting in a low voltage signal. As the throttle opens, the resistance decreases, causing the voltage signal to rise proportionally. The electronic control unit interprets this voltage signal to determine throttle position and adjust engine parameters accordingly. In non-contact TPS, a rotating magnet generates a changing magnetic field, which is detected by a Hall-effect sensor.
This produces an output voltage signal corresponding to the throttle valve position, when the throttle plate is opened, the magnetic field strength detected by the hall effect sensor changes, the electronic control unit processes this signal to control the engine function. Throttle position sensors are found in a variety of internal combustion engines, including automobiles, motorcycles, boats, and other vehicles. They are vital components of electronic fuel injection systems and electronic throttle control systems, enabling precise control of engine performance and emissions.
The combination of throttle position sensors brings many benefits to modern automotive systems. The throttle position sensor enables the electronic control unit to optimize the air-fuel mixture and ignition timing for different driving conditions by providing accurate throttle position data, thereby effectively Helping improve engine performance. By precisely controlling the air-fuel ratio, TPS helps improve fuel efficiency, resulting in lower fuel consumption and emissions.
The main function
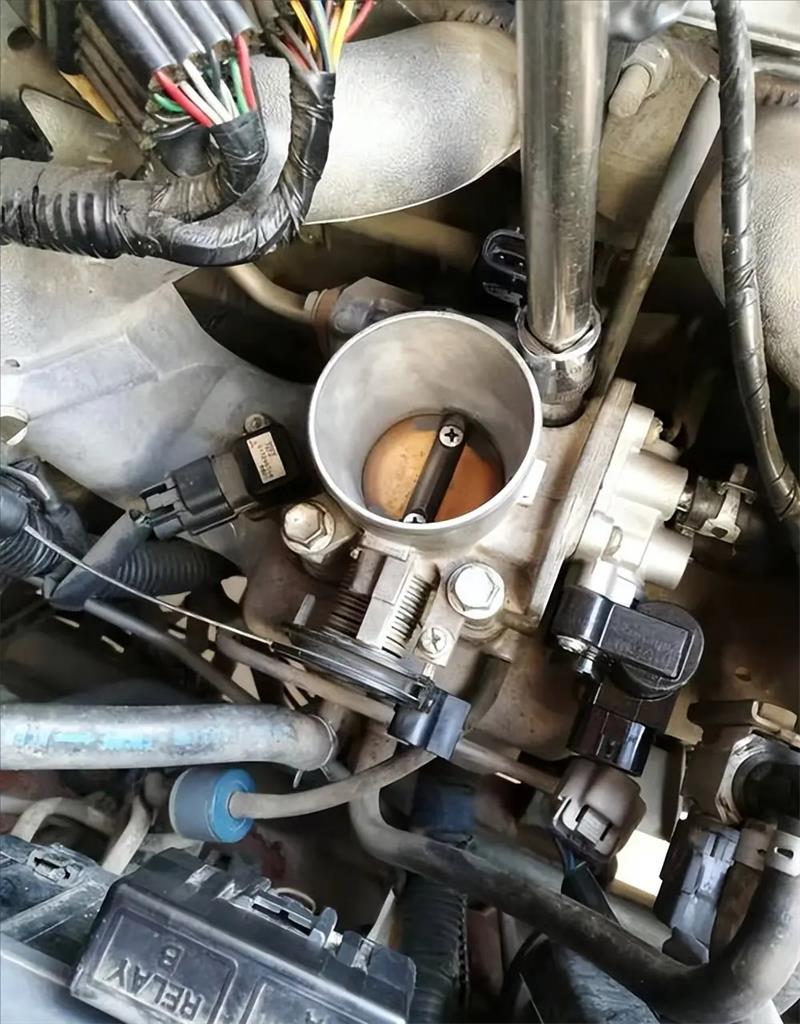
At the heart of its function, the throttle position sensor detects the position of the throttle plate, which opens or closes when the driver depresses the gas pedal, regulating the amount of air entering the engine’s intake manifold. A throttle position sensor mounted on the throttle body or attached to the throttle shaft precisely tracks the movement of the throttle blade and converts it to an electrical signal, usually a voltage or a resistance value. This signal is then sent to the ECU, which uses the data to make real-time adjustments to engine parameters.
One of the key functions of the TPS is to help the ECU determine the engine load. By correlating the throttle position with other engine parameters such as engine speed (RPM) and intake manifold pressure (MAP), the ECU can accurately calculate the load on the engine. Engine load data is critical to determining the required fuel injection duration, ignition timing and other performance related aspects. This information enables the electronic control unit to optimize the air-fuel mixture.
In modern vehicles equipped with Electronic Throttle Control (ETC), TPS helps facilitate communication between the driver’s accelerator pedal input and the engine’s throttle movement. In a conventional throttle system, the gas pedal is mechanically connected to the gas pedal by a cable. However, in the ETC system, the throttle valve is electronically controlled by the ECU according to the TPS data. This technology provides greater precision and responsiveness, enhancing the overall driving experience and safety.
Another important aspect of TPS is its role in engine diagnostics, the electronic control unit continuously monitors the TPS signal and compares it to other engine sensor readings. Any discrepancy or anomaly in the TPS data triggers a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) and illuminates the “check engine” light on the instrument panel. This helps mechanics identify potential issues related to the throttle system or other engine components for timely maintenance and repairs.
Post time: Aug-22-2023